In recent years, the adoption of drones in volumetrics has surged as advancements in technology have rendered it more cost-effective and attainable. Volumetrics, a subset of geospatial science, employs remote sensing methodologies to gauge, simulate, and scrutinize material volume.
This application finds utility in estimating the quantity of material necessitating removal (or addition) from a project site, gauging stockpiles and quarries, or assessing the land requirement for construction endeavors.
Conventional volumetric assessments entail a survey team and intricate estimations, presenting a time-consuming process that often takes weeks to compile reports and incurs substantial expenses. This method is susceptible to subjectivity and errors, yielding inaccurate or outdated outcomes.
Thankfully, drone technology has revolutionized volumetric calculations, enabling real-time assessments at a fraction of the cost and time compared to traditional approaches. The results are precise, with calculations promptly reported, and expenses significantly reduced compared to employing a survey team.
Moreover, traditional survey teams necessitate halting any work around the stockpile, potentially causing schedule disruptions and workflow delays. Drones mitigate safety risks, allowing onsite operations to continue uninterrupted.
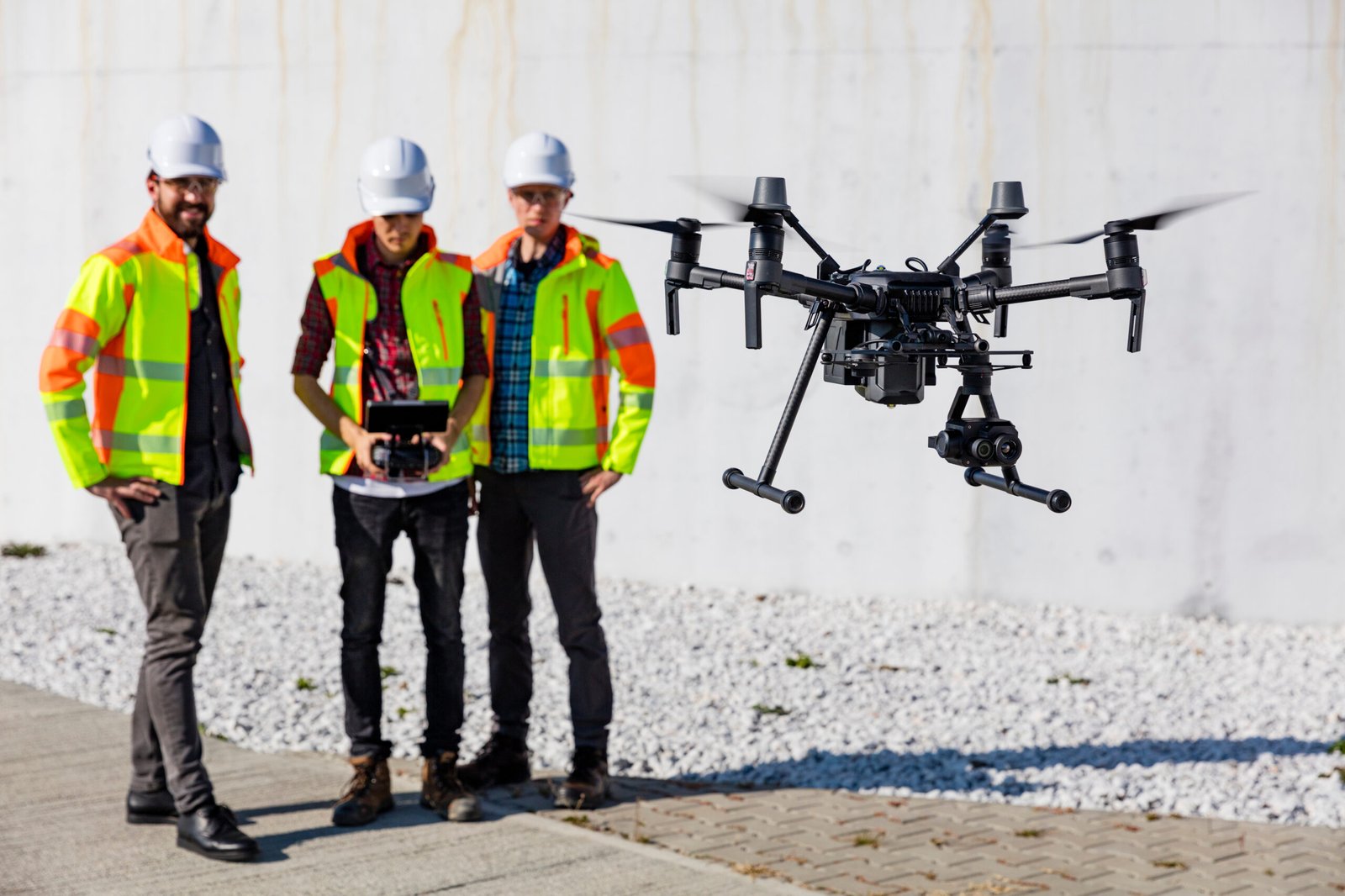

Drones present a convenient and efficient method for stockpile measurement, capable of swiftly and comprehensively covering extensive areas while capturing data from diverse perspectives. This capability proves particularly advantageous for stockpiles situated in inaccessible or perilous locations, facilitating measurements without requiring human presence in these areas.
Various methods exist for utilizing drones in stockpile measurement, with the following being the most prevalent:
Equipped with sensors like LiDAR or photogrammetry cameras, drones can capture images and gather data while flying over the stockpile. This collected data serves as the foundation for constructing a 3D model of the stockpile, facilitating volume calculations.
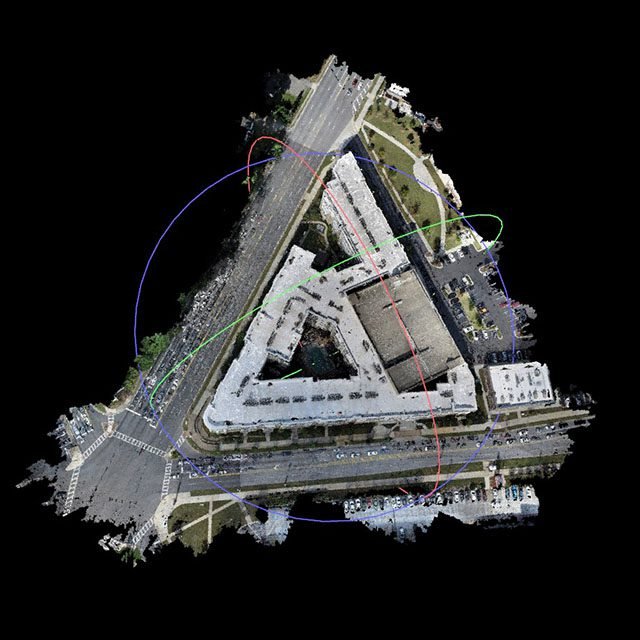
Detailed aerial imagery captured at high resolution can be utilized to generate 3D models, aiding the crew in identifying design challenges and pinpointing potential flaws early in the process, thereby avoiding unnecessary resource wastage. These 3D models serve as a valuable tool to ensure alignment with the original design blueprint and enable clients to visualize the projected outcome of the project.

These experts frequently employ drones to produce intricate maps and models of terrain and various natural elements. Leveraging these models, they can accurately determine the volume of objects, such as stockpiles of materials, through precise calculations.
Drones possess the capability to gauge the volume of crops and other vegetation, facilitating the monitoring of crop growth and development, along with estimating agricultural yields.
Drones are capable of measuring the volume of construction materials like concrete, gravel, sand, and other aggregates. This functionality aids in estimating quantities and associated costs for construction projects.
Increase safety – Because drones are controlled remotely, safety risks are significantly reduced
Avoid delays and changes in data –Report accurate and timely measurements using real-time data.
Speed – Cut down on hours of work and calculate measurements within minutes.
Affordability – Drone services are less expensive than survey teams.
Improve workflow – Work doesn’t have to be put on hold while collecting and calculating measurements, keeping you on schedule.
Confidence – No need to eyeball volumetric measurements again. Provide accurate data every time.
Let DFW AirView assure you that your project site is providing accurate data and adhering to the schedule without the risk of delays and workflow disruptions. Set the standard for volumetric measurements.
Better data leads to more informed decisions.